
For Msc In Business Objects Client
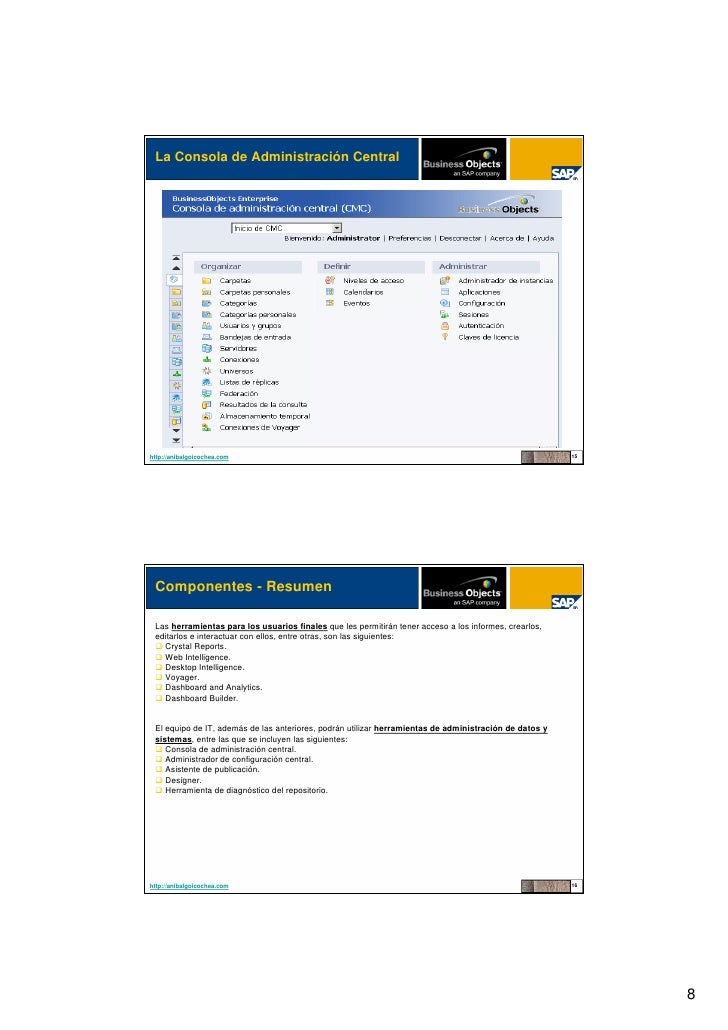
Students in the 30-credit Master of Science in Business Intelligence & Analytics program are exposed to the latest applications and theories that add value to any organization through data, information, knowledge, processes, and communications technologies. Built on the certification standards of SAS, Inc., the industry-leading Business Intelligence software provider, the curriculum of the degree from Saint Joseph’s University covers data mining, data warehousing, and data-driven communication to help graduates master front-to-back Business Intelligence and Analytics skills, something few other schools can offer.
Choose from one of four tracks based on your career goals: General Track, Cyber Analytics, Data Analysis, or Programming Languages. Graduates will receive not only the Business Intelligence & Analytics master’s degree, but a Business Intelligence Certificate endorsed by SAS, Inc., as well.
The aim of this course is to provide the student with an understanding of several management science techniques and to provide some insight into how these tools may be used to analyze complex business problems and arrive at a rational solution. The techniques to be studied are forecasting, linear planning, simulation, and modeling. Cases of increasing complexity will be used to emphasize problem description, definition, and formulation. The computer will be used extensively throughout the course, primarily by using available programs to perform the calculations after the problem has been correctly formulated. Emphasis will be placed on the interpretation and implementation of results.
In addition, we will examine the future of analytics. Prerequisite: DSS 600 and 100% ALEKS completion.
Traditional database design concentrates on the functional areas of business and their database needs. At the strategic and value-chain levels, we look at data across the enterprise and over time. The issues of Enterprise Data in the Data Warehouse, Data Marts, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Supply Chain Management (SCM), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), and the concepts of Data Mining will be surveyed in this course. Prerequisites: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 630. This course extends the data mining process to the predictive modeling, model assessment, scoring, and implementation stages. In this course, professional data mining software and small and large data sets will be used to effectively analyze and communicate statistical patterns in underlying business data for strategic management decision making.
Prerequisites: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 660. Programming Languages students must select this course, which is required for SAS Certification, OR DSS 620. The aim of this course is to provide the student with an understanding of several management science techniques and to provide some insight into how these tools may be used to analyze complex business problems and arrive at a rational solution.
The techniques to be studied are forecasting, linear planning, simulation, and modeling. Cases of increasing complexity will be used to emphasize problem description, definition, and formulation. The computer will be used extensively throughout the course, primarily by using available programs to perform the calculations after the problem has been correctly formulated.
Emphasis will be placed on the interpretation and implementation of results. In addition, we will examine the future of analytics. Prerequisite: DSS 600 and 100% ALEKS completion. The goal of this course will be to use R’s command line interface (CLI) to build familiarity with the basic R toolkit for statistical analysis and graphics. Specifically, students will learn good programming practices to manage and manipulate data, become familiar with some of R's most commonly used statistical procedures, and apply knowledge of data mining techniques (Multivariate Statistics, Regression, ANOVA, Cluster Analysis, Logistic Regression) for complex data sets using R. Prerequisite: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 660. Python is an open source programming language that focuses on readability, coherence and software quality.
It boosts developer productivity beyond compiled or statically typed languages and is portable to all major computing platforms. This course is designed as an introduction to python programming and the characteristics that make it unique.
Student will learn the use of the python interpreter, how to run programs, python object types, python numeric types, dynamic typing, string fundamentals, lists and dictionaries, and tuples and files. Prerequisite DSS 600, DSS 610. This course introduces students to the interdisciplinary field of cybersecurity by discussing the evolution of information security into cybersecurity, cybersecurity theory, and the relationship of cybersecurity to nations, businesses, society, and people. Students will be exposed to multiple cybersecurity technologies, processes, and procedures, learn how to analyze the threats, vulnerabilities and risks present in these environments, and develop appropriate strategies to mitigate potential cybersecurity problems. Prerequisite: DSS 600, DSS 610. This course introduces students to the CPS Framework, which was developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in an effort to facilitate a shared understanding of cyber-physical systems, their foundational concepts and their unique dimensions. Cyber-physical systems are smart systems that include interacting networks of physical and computational components.
They are widely recognized as having great potential to enable innovative applications and impact multiple economic sectors in the worldwide economy. Through the use of a shared vocabulary, the CPS Framework facilitates a thorough analysis of complex systems and processes, the uncovering of dependencies, weaknesses, risks, and the identification of corrective actions, both within the cyber domain and outside of it. Prerequisite: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 750. The aim of this course is to provide the student with an understanding of several management science techniques and to provide some insight into how these tools may be used to analyze complex business problems and arrive at a rational solution.
The techniques to be studied are forecasting, linear planning, simulation, and modeling. Cases of increasing complexity will be used to emphasize problem description, definition, and formulation. The computer will be used extensively throughout the course, primarily by using available programs to perform the calculations after the problem has been correctly formulated.
Emphasis will be placed on the interpretation and implementation of results. In addition, we will examine the future of analytics. Prerequisite: DSS 600 and 100% ALEKS completion. Python is an open source programming language that focuses on readability, coherence and software quality.
It boosts developer productivity beyond compiled or statically typed languages and is portable to all major computing platforms. This course is designed as an introduction to python programming and the characteristics that make it unique.
Student will learn the use of the python interpreter, how to run programs, python object types, python numeric types, dynamic typing, string fundamentals, lists and dictionaries, and tuples and files. Prerequisite DSS 600, DSS 610.
The goal of this course will be to use R’s command line interface (CLI) to build familiarity with the basic R toolkit for statistical analysis and graphics. Specifically, students will learn good programming practices to manage and manipulate data, become familiar with some of R's most commonly used statistical procedures, and apply knowledge of data mining techniques (Multivariate Statistics, Regression, ANOVA, Cluster Analysis, Logistic Regression) for complex data sets using R.
Prerequisite: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 660. This course extends the data mining process to the predictive modeling, model assessment, scoring, and implementation stages.
In this course, professional data mining software and small and large data sets will be used to effectively analyze and communicate statistical patterns in underlying business data for strategic management decision making. Prerequisites: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 660. Programming Languages students must select this course, which is required for SAS Certification, OR DSS 620. The aim of this course is to provide the student with an understanding of several management science techniques and to provide some insight into how these tools may be used to analyze complex business problems and arrive at a rational solution. The techniques to be studied are forecasting, linear planning, simulation, and modeling. Cases of increasing complexity will be used to emphasize problem description, definition, and formulation. The computer will be used extensively throughout the course, primarily by using available programs to perform the calculations after the problem has been correctly formulated.
Emphasis will be placed on the interpretation and implementation of results. In addition, we will examine the future of analytics. Prerequisite: DSS 600 and 100% ALEKS completion. Python is an open source programming language that focuses on readability, coherence and software quality.
It boosts developer productivity beyond compiled or statically typed languages and is portable to all major computing platforms. This course is designed as an introduction to python programming and the characteristics that make it unique. Student will learn the use of the python interpreter, how to run programs, python object types, python numeric types, dynamic typing, string fundamentals, lists and dictionaries, and tuples and files. Prerequisite DSS 600, DSS 610. Traditional database design concentrates on the functional areas of business and their database needs. At the strategic and value-chain levels, we look at data across the enterprise and over time.
Mac Computers For Business
The issues of Enterprise Data in the Data Warehouse, Data Marts, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Supply Chain Management (SCM), Customer Relationship Management (CRM), Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), and the concepts of Data Mining will be surveyed in this course. Prerequisites: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 630. The goal of this course will be to use R’s command line interface (CLI) to build familiarity with the basic R toolkit for statistical analysis and graphics. Specifically, students will learn good programming practices to manage and manipulate data, become familiar with some of R's most commonly used statistical procedures, and apply knowledge of data mining techniques (Multivariate Statistics, Regression, ANOVA, Cluster Analysis, Logistic Regression) for complex data sets using R.
Best Mac For Business
Prerequisite: DSS 600, DSS 610, DSS 660.